Scalability is one of the core benefits of Kubernetes (K8s). In order to get the most out of this benefit (and use K8s effectively), you need a solid understanding of how Kubernetes autoscaling works. In our previous post[link], we covered Vertical Pod Autoscaling (VPA). Here, we’ll take a deep dive on the topic of Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA) in Kubernetes. We’ll define HPA, explain how it works, and provide a detailed hands-on tutorial to walk you through a sample project using HPA.
Chapter 2:
Kubernetes HPA
Kubernetes autoscaling basics
Before we go in-depth on HPA, we need to review Kubernetes autoscaling in general. Autoscaling is a method of automatically scaling K8s workloads up or down based on historical resource usage. Autoscaling in Kubernetes has three dimensions:
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA):adjusts the number of replicas of an application.
- Cluster Autoscaler:adjusts the number of nodes of a cluster.
- Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA):adjusts the resource requests and limits of a container.
The different autoscalers work at one of two Kubernetes layers
- Pod level:The HPA and VPA methods take place at the pod level. Both HPA and VPA will scale the available resources or instances of the container.
- Cluster level:The Cluster Autoscaler falls under the Cluster level, where it scales up or down the number of nodes inside your cluster.
Now that we have summarized the basics, let’s take a closer look at HPA.
What is HPA?
HPA is a form of autoscaling that increases or decreases the number of pods in a replication controller, deployment, replica set, or stateful set based on CPU utilization—the scaling is horizontal because it affects the number of instances rather than the resources allocated to a single container.
HPA can make scaling decisions based on custom or externally provided metrics and works automatically after initial configuration. All you need to do is define the MIN and MAX number of replicas.
Once configured, the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler controller is in charge of checking the metrics and then scaling your replicas up or down accordingly. By default, HPA checks metrics every 15 seconds.
To check metrics, HPA depends on another Kubernetes resource known as the Metrics Server. The Metrics Server provides standard resource usage measurement data by capturing data from “kubernetes.summary_api” such as CPU and memory usage for nodes and pods. It can also provide access to custom metrics (that can be collected from an external source) like the number of active sessions on a load balancer indicating traffic volume.
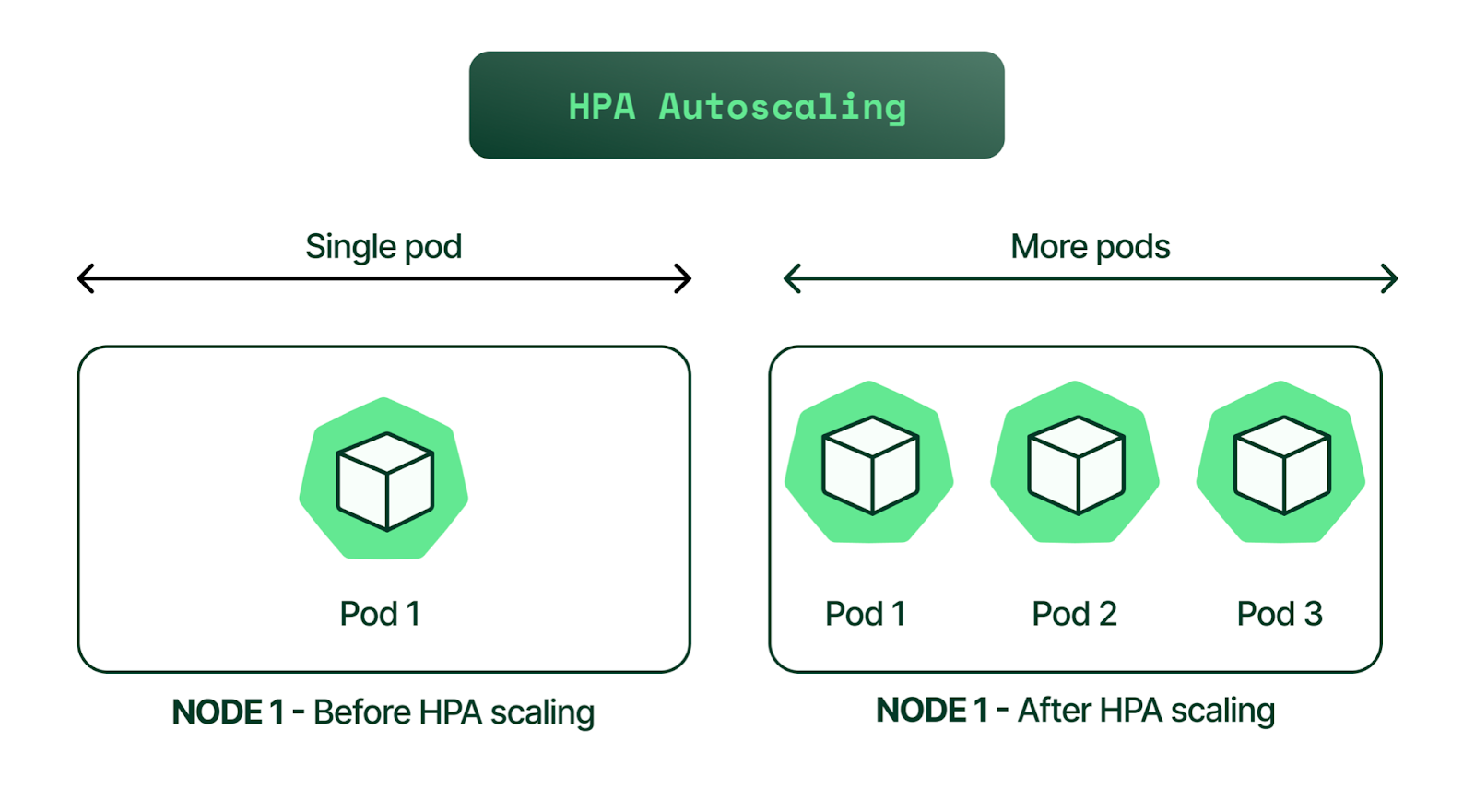
While the HPA scaling process is automatic, you can also help account for predictable load fluctuations in some cases. For example, you can:
- Adjust replica count based on the time of the day.
- Set different capacity requirements for weekends or off-peak hours.
- Implement an event-based replica capacity schedule (such as increasing capacity upon a code release).
How does HPA work?
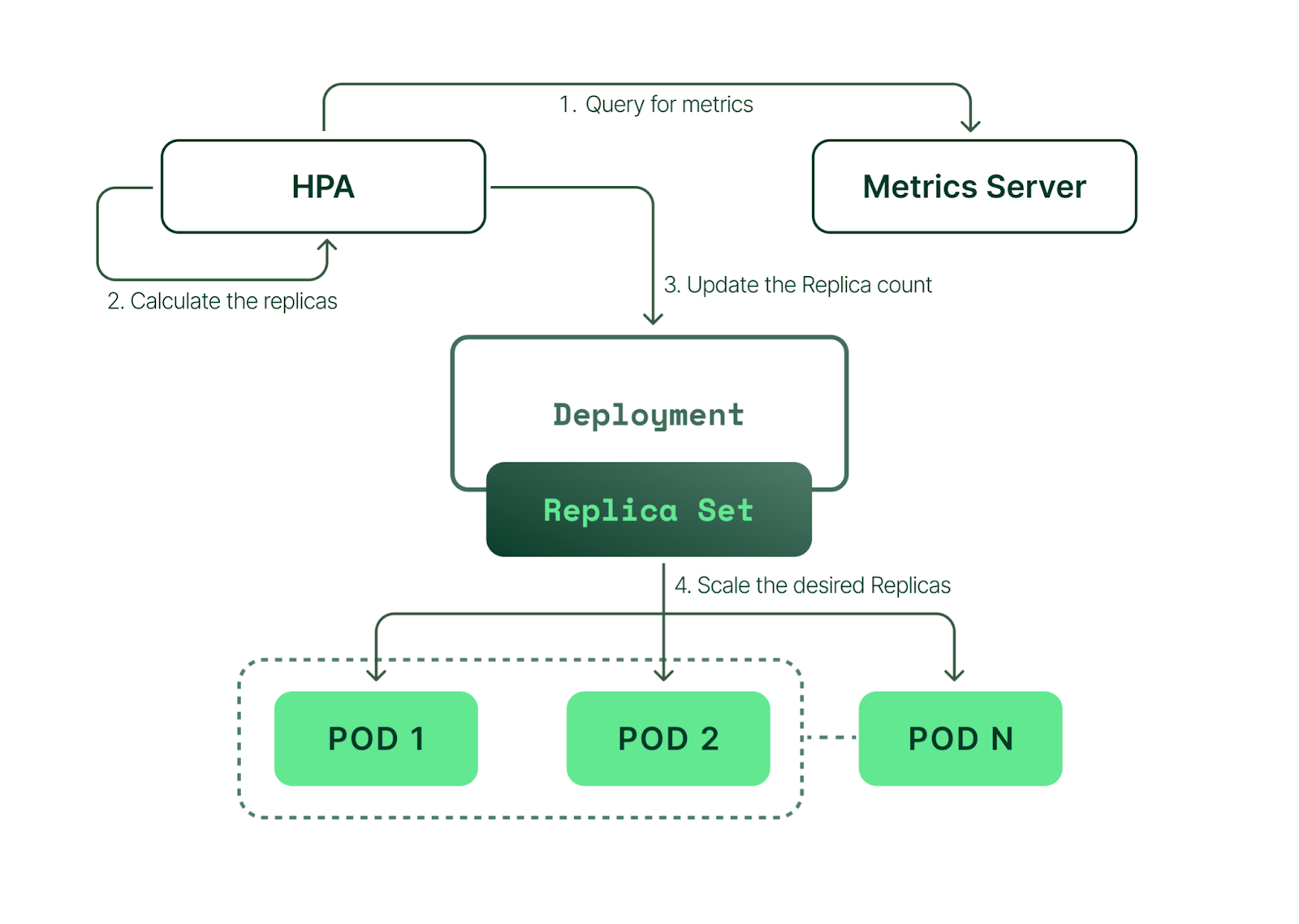
Overview of HPA
In simple terms, HPA works in a “check, update, check again” style loop. Here’s how each of the steps in that loop work.
- HPA continuously monitors the metrics server for resource usage.
- Based on the collected resource usage, HPA will calculate the desired number of replicas required.
- Then, HPA decides to scale up the application to the desired number of replicas.
- Finally, HPA changes the desired number of replicas.
- Since HPA is continuously monitoring, the process repeats from Step 1.
Limitations of HPA
While HPA is a powerful tool, it’s not ideal for every use case and can’t address every cluster resource issue. Here are the most common examples:
- One of HPA’s most well-known limitations is that it does not work with DaemonSets.
- If you don’t efficiently set CPU and memory limits on pods, your pods may terminate frequently or, on the other end of the spectrum, you’ll waste resources.
- If the cluster is out of capacity, HPA can’t scale up until new nodes are added to the cluster. Cluster Autoscaler (CA) can automate this process. We have an article dedicated to CA; however, below is a quick contextual explanation.
Cluster Autoscaler (CA) automatically adds or removes nodes in a cluster based on resource requests from pods. Unlike HPA, Cluster Autoscaler doesn't look at memory or CPU available when it triggers the autoscaling. Instead, Cluster Autoscaler reacts to events and checks for any unscheduled pods every 10 seconds.
Comprehensive Kubernetes cost monitoring & optimization
EKS Example: How to Implement HPA
To help you get started with HPA, let’s walk through some practical examples. We’ll work through the following steps one-by-one:
- Create an EKS cluster
- Install the Metrics Server
- Deploy a sample application
- Install Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
- Monitor HPA events
- Decrease the load
Step 1: create an EKS cluster
For this step, we will use AWS EKS (Amazon's managed Kubernetes service), so make sure you have access to your AWS account. We’ll use eksctl, a simple CLI tool for creating and managing clusters on EKS. It is written in Go and uses CloudFormation in the background.
The EKS cluster kubeconfig file will be stored in the local directory (of your workstation or laptop), and if the command is successful, you will see a ready status. To begin, we’ll run the eksctl create cluster command below (using Kubernetes version 1.20 in this example).
$ eksctl create cluster --name example-hpa-autoscaling --version 1.20 --region us-west-2 --nodegroup-name hpa-worker-instances --node-type c5.large --nodes 1
2021-08-30 12:52:24 [ℹ] eksctl version 0.60.0
2021-08-30 12:52:24 [ℹ] using region us-west-2
2021-08-30 12:52:26 [ℹ] setting availability zones to [us-west-2a us-west-2b us-west-2d]
2021-08-30 12:52:26 [ℹ] subnets for us-west-2a - public:192.168.0.0/19 private:192.168.96.0/19
2021-08-30 12:52:26 [ℹ] subnets for us-west-2b - public:192.168.32.0/19 private:192.168.128.0/19
2021-08-30 12:52:26 [ℹ] subnets for us-west-2d - public:192.168.64.0/19 private:192.168.160.0/19
2021-08-30 12:52:26 [ℹ] nodegroup "hpa-worker-instances" will use "" [AmazonLinux2/1.20]
2021-08-30 12:52:26 [ℹ] using Kubernetes version 1.20
2021-08-30 12:52:26 [ℹ] creating EKS cluster "example-hpa-autoscaling" in "us-west-2" region with managed nodes
...
...
2021-08-30 12:53:29 [ℹ] waiting for CloudFormation stack
2021-08-30 13:09:00 [ℹ] deploying stack "eksctl-example-hpa-autoscaling-nodegroup-hpa-worker-instances"
2021-08-30 13:09:00 [ℹ] waiting for CloudFormation stack
2021-08-30 13:12:11 [ℹ] waiting for the control plane availability...
2021-08-30 13:12:11 [✔] saved kubeconfig as "/Users/karthikeyan/.kube/config"
2021-08-30 13:12:11 [ℹ] no tasks
2021-08-30 13:12:11 [✔] all EKS cluster resources for "example-hpa-autoscaling" have been created
2021-08-30 13:12:13 [ℹ] nodegroup "hpa-worker-instances" has 1 node(s)
2021-08-30 13:12:13 [ℹ] node "ip-192-168-94-150.us-west-2.compute.internal" is ready
2021-08-30 13:12:13 [ℹ] waiting for at least 1 node(s) to become ready in "hpa-worker-instances"
2021-08-30 13:12:13 [ℹ] nodegroup "hpa-worker-instances" has 1 node(s)
2021-08-30 13:12:13 [ℹ] node "ip-192-168-94-150.us-west-2.compute.internal" is ready
2021-08-30 13:14:20 [ℹ] kubectl command should work with "/Users/karthikeyan/.kube/config", try 'kubectl get nodes'
2021-08-30 13:14:20 [✔] EKS cluster "example-hpa-autoscaling" in "us-west-2" region is ready
Next, verify the cluster:
$ aws eks describe-cluster --name my-hpa-demo-cluster --region us-west-2You can also check by logging into the AWS console:
To get the cluster context to log in, read your local kubeconfig like below:
$ cat ~/.kube/config |grep "current-context"
current-context: bob@my-hpa-demo-cluster.us-west-2.eksctl.ioList the nodes and pods:
$ kubectx bob@example-hpa-autoscaling.us-west-2.eksctl.io
Switched to context "bob@example-hpa-autoscaling.us-west-2.eksctl.io".
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ip-192-168-94-150.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready 15m v1.20.4-eks-6b7464
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system aws-node-f45pg 1/1 Running 0 15m
kube-system coredns-86d9946576-2h2zk 1/1 Running 0 24m
kube-system coredns-86d9946576-4cvgk 1/1 Running 0 24m
kube-system kube-proxy-864g6 1/1 Running 0 15m kubectx is a tool used to switch between various Kubernetes clusters. Now that we have the EKS cluster up and running, next, we need to deploy the Metrics Server.
Install the Metrics Server
We can check if we have set up the Metrics Server in our EKS cluster by using the following command:
$ kubectl top pods -n kube-system
error: Metrics API not available📝 Note: For this process, we have created a directory named “/Users/bob/hpa/” on our local laptop and saved all configuration files used in this article to that location. We recommend creating a similar directory on your local workstation to download all required files (mentioned below).
Let’s install the Metrics Server. Download the YAML files from: https://github.com/nonai/k8s-example-files/tree/main/metrics-server
$ cd /Users/bob/hpa/metrics-server && ls -l
total 56
-rw-r--r-- 1 bob 1437157072 136 Aug 30 13:48 0-service-account.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 bob 1437157072 710 Aug 30 13:48 1-cluster-roles.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 bob 1437157072 362 Aug 30 13:48 2-role-binding.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 bob 1437157072 667 Aug 30 13:48 3-cluster-role-bindings.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 bob 1437157072 254 Aug 30 13:48 4-service.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 bob 1437157072 1659 Aug 30 13:48 5-deployment.yaml
-rw-r--r-- 1 bob 1437157072 331 Aug 30 13:48 6-api-service.yamlOnce you have downloaded the file, run the below command to create all of the resources:
$ kubectl apply -f .
serviceaccount/metrics-server created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:aggregated-metrics-reader created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server-auth-reader created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/metrics-server:system:auth-delegator created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/system:metrics-server created
service/metrics-server created
deployment.apps/metrics-server created
apiservice.apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io createdVerify the Metrics Server deployment:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system aws-node-982kv 1/1 Running 0 14m
kube-system aws-node-rqbg9 1/1 Running 0 13m
kube-system coredns-86d9946576-9k6gx 1/1 Running 0 25m
kube-system coredns-86d9946576-m67h6 1/1 Running 0 25m
kube-system kube-proxy-lcklc 1/1 Running 0 13m
kube-system kube-proxy-tk96q 1/1 Running 0 14m
kube-system metrics-server-9f459d97b-q5989 1/1 Running 0 41sList services in the kube-system namespace:
$ kubectl get svc -n kube-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kube-dns ClusterIP 10.100.0.10 53/UDP,53/TCP 26m
metrics-server ClusterIP 10.100.66.231 443/TCP 82s Use kubectl to see CPU and memory metrics:
$ kubectl top pods -n kube-system
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
aws-node-982kv 4m 40Mi
aws-node-rqbg9 5m 39Mi
coredns-86d9946576-9k6gx 2m 8Mi
coredns-86d9946576-m67h6 2m 8Mi
kube-proxy-lcklc 1m 11Mi
kube-proxy-tk96q 1m 11Mi
metrics-server-9f459d97b-q5989 3m 15MiDeploy a sample application
Now, we are going to use a custom Docker image that runs on Apache and PHP to… . The Docker image is publicly accessible, so we can refer to it directly from our Kubernetes deployment.
Let’s deploy the application as part of our Kubernetes cluster, maintaining a minimum of 1 replica and a maximum of 10 replicas. Below is the configuration, which you can save as “deployment.yml”.
$ cd /Users/bob/hpa/
$ cat deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hpa-demo-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
run: hpa-demo-deployment
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: hpa-demo-deployment
spec:
containers:
- name: hpa-demo-deployment
image: k8s.gcr.io/hpa-example
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
requests:
cpu: 200mApply it by running:
$ kubectl apply -f deployment.yml
deployment.apps/hpa-demo-deployment created
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hpa-demo-deployment-6b988776b4-b2hkb 1/1 Running 0 20sWe created the deployment successfully. Next, let’s get the list of deployment status:
$ kubectl get deploy
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hpa-demo-deployment 1/1 1 1 9sCreate the Kubernetes service
For our next step, we have to create a service. The sample application will listen to the public endpoint by using this service. Create a service configuration file with the following content:
$ cd /Users/bob/hpa/
$ cat service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hpa-demo-deployment
labels:
run: hpa-demo-deployment
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
selector:
run: hpa-demo-deploymentThis service will be a front-end to the deployment we created above, which we can access via port 80.
Apply the changes:
$ kubectl apply -f service.yaml
service/hpa-demo-deployment createdWe have created the service. Next, let’s list the service and see the status:
$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hpa-demo-deployment ClusterIP 10.100.124.139 80/TCP 7s
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.100.0.1 443/TCP 172m Here, we can see:
- hpa-demo-deployment = Service Name
- 10.100.124.139 = IP address of the service, and it is open on Port 80/TCP
Install the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
We now have the sample application as part of our deployment, and the service is accessible on port 80. To scale our resources, we will use HPA to scale up when traffic increases and scale down the resources when traffic decreases.
Let’s create the HPA configuration file as shown below:
$ cd /Users/bob/hpa/
$ cat hpa.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: hpa-demo-deployment
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: hpa-demo-deployment
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 50Apply the changes:
$ kubectl apply -f hpa.yaml
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/hpa-demo-deployment createdVerify the HPA deployment:
$ kubectl get hpa
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
hpa-demo-deployment Deployment/hpa-demo-deployment 0%/50% 1 10 0 8sThe above output shows that the HPA maintains between 1 and 10 replicas of the pods controlled by the hpa-demo-deployment. In the example shown above (see the column titled “TARGETS”), the target of 50% is the average CPU utilization that the HPA needs to maintain, whereas the target of 0% is the current usage.
If we want to change the MIN and MAX values, we can use this command:
📝Note: Since we already have the same MIN/MAX values, the output throws an error that says it already exists.
Increase the load
So far, we have set up our EKS cluster, installed the Metrics Server, deployed a sample application, and created an associated Kubernetes service for the application. We also deployed HPA, which will monitor and adjust our resources.
To test HPA in real-time, let’s increase the load on the cluster and check how HPA responds in managing the resources.
First, let’s check the current status of the deployment:
$ kubectl get deploy
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hpa-demo-deployment 1/1 1 1 23sNext, we will start a container and send an infinite loop of queries to the ‘php-apache’ service, listening on port 8080. Open a new terminal and execute the below command:
# kubectl run -i --tty load-generator --rm --image=busybox --restart=Never -- /bin/sh -c "while sleep 0.01; do wget -q -O- http://hpa-demo-deployment; done"📝Note: If you do not have DNS entries for the service, use the service name.
To view the service name:
$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
hpa-demo-deployment ClusterIP 10.100.95.188 80/TCP 10m Before we increase the load, the HPA status will look like this:
$ kubectl get hpa
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
hpa-demo-deployment Deployment/hpa-demo-deployment 0%/50% 1 10 1 12mOnce you triggered the load test, use the below command, which will show the status of the HPA every 30 seconds:
$ kubectl get hpa -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
hpa-demo-deployment Deployment/hpa-demo-deployment 0%/50% 1 10 1 15m
...
...
hpa-demo-deployment Deployment/hpa-demo-deployment 38%/50% 1 10 8 25mHere, you can see that as our usage went up, the number of pods scaled from 1 to 7:
$ kubectl get deployment php-apache
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hpa-demo-deployment 7/7 7 7 21mYou can also see pod usage metrics. The load-generator pod generates the load for this example:
$ kubectl top pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
default hpa-demo-deployment-6b988776b4-b2hkb 1m 10Mi
default load-generator 10m 1Mi
default hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68-2x89h 97m 12Mi
default hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68-5qxgm 86m 12Mi
default hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68-ddm54 131m 12Mi
default hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68-g6hhw 72m 12Mi
default hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68-pg67w 123m 12Mi
default hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68-rjp77 75m 12Mi
default hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68-vnd8k 102m 12Mi
kube-system aws-node-982kv 4m 41Mi
kube-system aws-node-rqbg9 4m 40Mi
kube-system coredns-86d9946576-9k6gx 4m 9Mi
kube-system coredns-86d9946576-m67h6 4m 9Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-lcklc 1m 11Mi
kube-system kube-proxy-tk96q 1m 11Mi
kube-system metrics-server-9f459d97b-q5989 4m 17MiMonitor HPA events
If you want to see what steps HPA is performing while scaling, use this command and check for the events section:
$ kubectl describe deploy hpa-demo-deployment
Name: hpa-demo-deployment
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 30 Aug 2021 17:15:34 +0530
Labels:
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
Selector: run=php-apache
Replicas: 7 desired | 7 updated | 7 total | 7 available | 0 NewReplicaSet: hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68 (7/7 replicas created)
...
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 12m deployment-controller Scaled up replica set hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68 to 1
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 5m39s deployment-controller Scaled up replica set hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68 to 4
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 5m24s deployment-controller Scaled up replica set hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68 to 5
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 4m38s deployment-controller Scaled up replica set hpa-demo-deployment-d4cf67d68 to 7 We can see that the pods were scaled up from 1 to 4, then to 5, and finally to 7.
Decrease the load
Next, we’ll decrease the load. Navigate to the terminal where you executed the load test and stop the load generation by entering
Then, verify the status of your resource usage:
$ kubectl get hpa
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
hpa-demo-deployment Deployment/hpa-demo-deployment 0%/50% 1 10 1 25m
$ kubectl get deployment hpa-demo-deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hpa-demo-deployment 1/1 1 1 25mAnother way to verify the status is:
$ kubectl get events51m Normal SuccessfulCreate replicaset/hpa-demo-deployment-cf6477c46 Created pod: hpa-demo-deployment-cf6477c46-b56vr
52m Normal SuccessfulRescale horizontalpodautoscaler/hpa-demo-deployment New size: 4; reason: cpu resource utilization (percentage of request) above target
52m Normal ScalingReplicaSet deployment/hpa-demo-deployment Scaled up replica set hpa-demo-deployment-cf6477c46 to 4
52m Normal SuccessfulRescale horizontalpodautoscaler/hpa-demo-deployment New size: 6; reason: cpu resource utilization (percentage of request) above target
52m Normal ScalingReplicaSet deployment/hpa-demo-deployment Scaled up replica set hpa-demo-deployment-cf6477c46 to 6
51m Normal SuccessfulRescale horizontalpodautoscaler/hpa-demo-deployment New size: 7; reason: cpu resource utilization (percentage of request) above target
51m Normal ScalingReplicaSet deployment/hpa-demo-deployment Scaled up replica set hpa-demo-deployment-cf6477c46 to 7
53m Normal Scheduled pod/load-generator Successfully assigned default/load-generator to ip-192-168-74-193.us-west-2.compute.internal
53m Normal Pulling pod/load-generator Pulling image "busybox"
52m Normal Pulled pod/load-generator Successfully pulled image "busybox" in 1.223993555s
52m Normal Created pod/load-generator Created container load-generator
52m Normal Started pod/load-generator Started container load-generatorDestroy the cluster
Finally, we’ll destroy the demo EKS cluster with this command:
$ eksctl delete cluster --name my-hpa-demo-cluster --region us-west-2
2021-08-30 20:10:09 [ℹ] eksctl version 0.60.0
2021-08-30 20:10:09 [ℹ] using region us-west-2
2021-08-30 20:10:09 [ℹ] deleting EKS cluster "my-hpa-demo-cluster"
...
...
2021-08-30 20:12:40 [ℹ] waiting for CloudFormation stack "eksctl-my-hpa-demo-cluster-nodegroup-ng-1"
2021-08-30 20:12:41 [ℹ] will delete stack "eksctl-my-hpa-demo-cluster-cluster"
2021-08-30 20:12:42 [✔] all cluster resources were deleted
Usage and cost reporting with HPA
With increased scalability comes increased complexity—horizontal autoscaling complicates usage and cost reporting by introducing variability into the equation. Usage is easier to measure and attribute to each tenant in a Kubernetes cluster when capacity is absolutely static and the cluster has no more than a couple of tenants. However, as you add more tenants and constantly adjust the capacity (as HPA allows us to do), specialized tooling becomes a must-have for allocating costs to tenants.
The open-source Kubecost tool solves this problem by measuring detailed usage by Kubernetes concept, and correlating granular usage data with billing information from your cloud provider or cost estimates from your on-prem environment.
It’s easier to measure usage and calculate costs in a static Kubernetes cluster. It’s much harder to do it when the resources allocated to pods routinely change.
The main Kubecost dashboard shown below summarizes cluster costs, efficiency, and the health of your clusters:
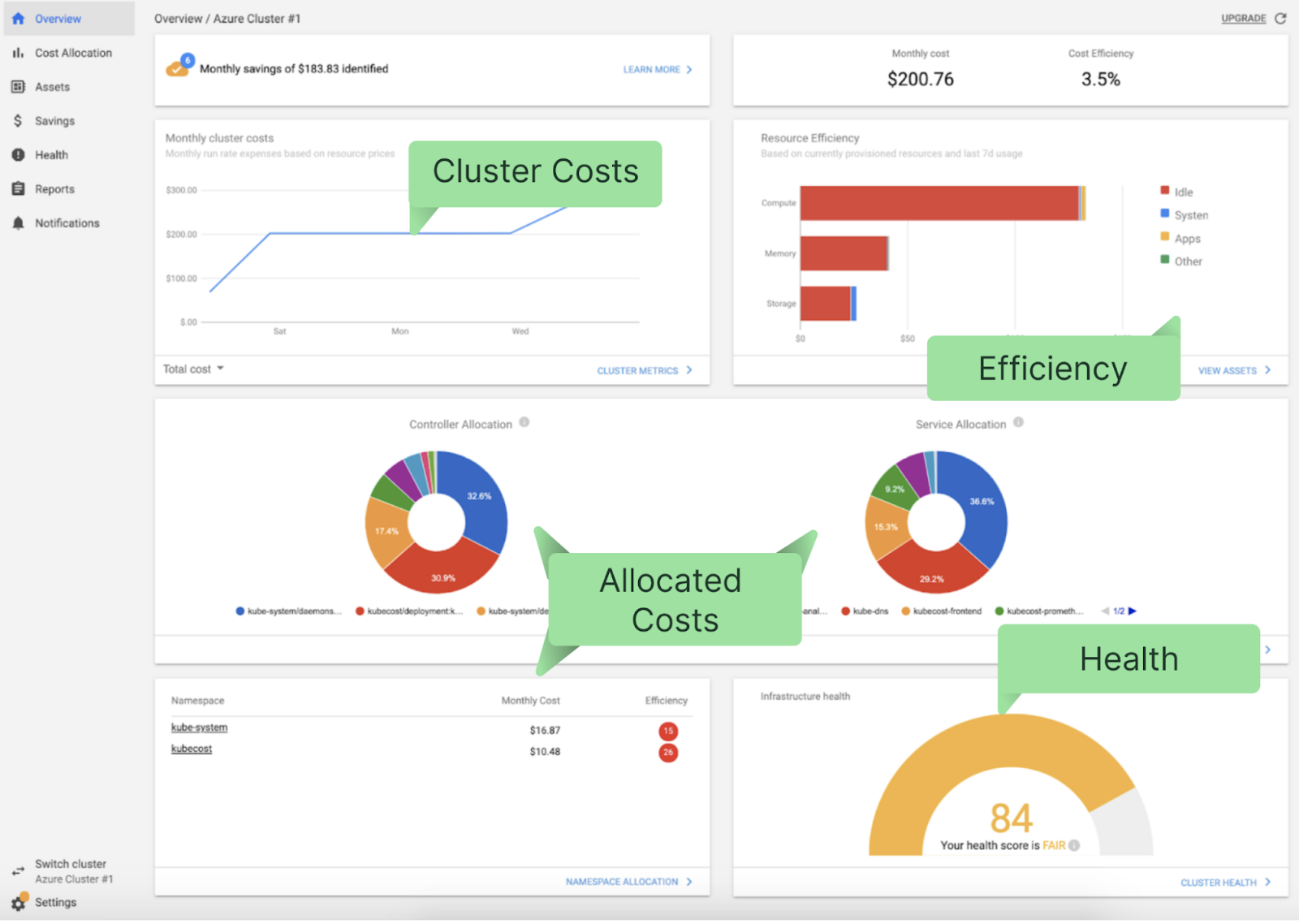
A single Helm command installs Kubecost. You can start here and try it out for free.
Summary
To recap, in this article, we have learned:
- HPA is one of the autoscaling methods native to Kubernetes, used to scale resources like deployments, replica sets, replication controllers, and stateful sets. It increases or reduces the number of pods based on observed metrics and in accordance with given thresholds.
- Each HPA exists in the cluster as a HorizontalPodAutoscaler object. To interact with these objects, you can use commands like “kubectl get hpa” or “kubectl describe hpa HPA_NAME”.
- HPA makes scaling decisions based on resource request values at the container level. Therefore, it is essential to have configured the resource request values for all of your containers.
- The Metrics Server must be installed on the Kubernetes cluster for HPA to work.
- Due to its inherent limitations, HPA works best when combined with Cluster Autoscaler. When the existing nodes on the cluster are exhausted, HPA cannot scale resources up, so it needs Cluster Autoscaler to help add nodes in the Kubernetes cluster.
